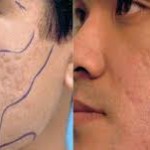
 Acne Scars or scarring occurs when collagen grows under the skin as an outcome of wound healing. This happens because of skin injuries that cause an unusual healing response.
Acne Scars or scarring occurs when collagen grows under the skin as an outcome of wound healing. This happens because of skin injuries that cause an unusual healing response.
There are different types of scars. The most common is the one that we can see on our faces or the so called acne scars. Often this happens in puberty when one can’t fight the urge to prick skin break-outs. It might also be caused by wounds from allergic reactions when we experiment with different facial products. Anyone can have this. Majority of people get the other types of scars while working in the garden, lawn, doing households chores and through other activities. There is always a way of preventing scarring by taking the correct vitamins, wearing gloves or a protective gear especially when we have to do something outdoors. Big scars can also be a result of an operation or an accident. A lot of individuals suffer emotional and psychological distress because of scars. That is why it is important to find ways of improving its appearance or removing them.
Acne Treatment: Go for the natural way
It is true that it’s difficult to remove scars but there are a lot of products in the market to treat this. Self confidence can be lost when you have acne scars especially when you’re in your teenage years. This can also cause pain and lack of comfort.
If you’re not up for laser treatment and ointments, consider adding zinc in your diet. Parents don’t fret. You don’t have to spend on expensive derma fees for your teenager just yet. Moderate cases of acne can be treated by taking zinc supplements. In fact, many have reported that within three days, their skin became less oily and the bumps were also reduced. Taking a zinc supplement for at least two weeks can clear up the skin by as much as 80%. It also prevents new acne from developing. However, consider a trial period of two to three days. Some stomachs are more sensitive than others and if it’s your child’s first time to take supplements, be more observant. It is still best to consult your doctor before starting supplementation.
Zinc for Scars
Zinc is one of the most neglected nutrients. We need to be aware that it is critical to our entire immune system and in the repair process of our bodies. A lot of people are not aware of the benefits of zinc.
Having acne and skin problems are two of the most common symptoms of zinc deficiency. Studies have shown that if you have enough zinc in your system there’s a good chance of having beautiful skin. It is also proven that zinc is good for acne. One of the major benefits of this mineral is that it helps our body repair tissues. By taking zinc your pimples can heal at a faster rate. Experts say that it is recommended to take around 50mg a day, to avoid acne scarring and preventing it from getting worse. Studies have shown that as we grow older, our zinc levels decline. This is in comparison to younger people. That is why when adults get wounds and scars, the healing process is slower. Healing rate is largely determined by the zinc levels that we have on our skin.


Leave a Reply